Basics of Semantics
Josef Noll
Introduction
- review of first lecture
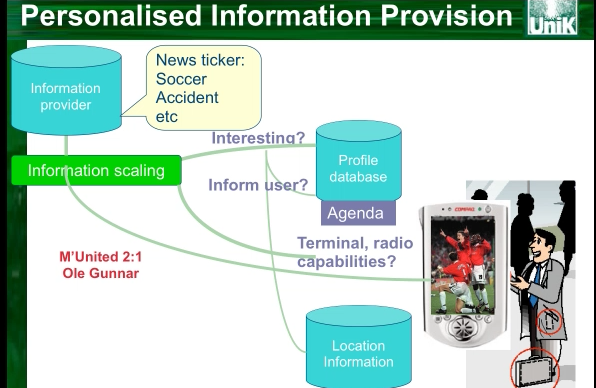
- context-aware, personalised
- Example: Media:PersonalisedInformation.mp4
- future "mobile" Internet: Web, People, Devices
Tasks
- Presentation of context aware scenarios
- 4-5 Scientific papers
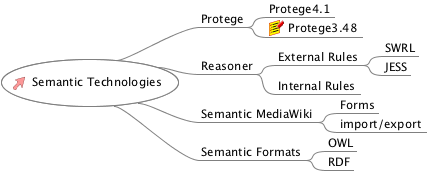
- install Protege 3.5
What are you going to learn:
- Understand the need for semantics
- Can list the basic elements of semantic technologies
- Explain the differences between semantic web and semantic web services
- Next: Identify semantic technologies for description of the user and his context
- Next: Describe the difference between ontologies and rules
Reference: J.C. Morris, The Role Of Ontology In Modern Expert Systems Dallas 2008, slideshare.com
Semantic Technologies
References:
Tim Berners Lee on Semantic Web
published in 2008
An introduction to the semantic Web
And some more fun - Ordering of a Pizza in the future
Discussion: Tagging versus Semantics
Usage of Semantic today
Customer preferences
- Trust relation
- Clear value proposition (convenience)
- Information/advertisement overload
Main duties for service players
- Customer relation (paying the bill)
- Service integration
- New business ideas
- Customer protection (information
References:
- J. Noll, "Semantics and Real World Multimedia", May 2008 Media:200805FIT-IT-SemanticsMultiMedia.pdf
Detailed intro to Semantics and Ontologies
See Service Semantics, Tutorial at LUT, Media:200708ServiceSemantics-Tutorial.pdf
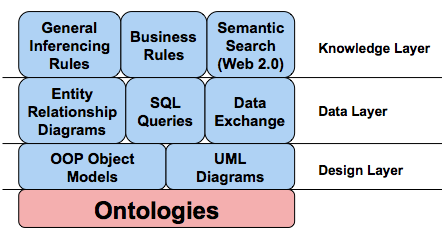
Fundamentals of Semantics
- Explain: RDF, OWL, ...
- Discuss: use cases, restrictions
Semantics:
- .xml relation between subject & object
- .rdf subject, predict, object
- .rdfs vocabulary for properties
- ontologies as data models of a domain
- describe through rdf or owl
- owl is more expressive
- Extension of semantics through rules
- Rules might replace ontologies
Challenges with ontologies
- ontologies describe the data on a Web
- very good suited as a knowledge base, e.g. medical history, interworking of medicine, oil drilling
- when using a semantic model in the real world, the challenge is to get changes (updates) to the ontologies. Example: car industry, where cars are produced under the same header with slightly different outfit, where manufacturers change frequently,...
Summary on Ontologies
- cover only limited area (specific area, "swamps of ontologies")
- have a "creation date" (timestamp) in mind
- upgradability?
- consistency when upgrading one ontology
- are good for knowledge management
- interface between knowledge management and processes is not clear
What have we learned, discuss
- Understand the need for semantics
- Can list the basic elements of semantic technologies
- Explain the differences between semantic web and semantic web services
- Next: Identify semantic technologies for description of the user and his context
- Next: Describe the difference between ontologies and rules
Tasks
- Presentation of context aware scenarios
- 4-5 Scientific papers
- install Protege 3.5
__