Reasoning
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
Josef Noll
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
Reasoner
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
The goal of a reasoner is to derive information from a knowledge base. The reasoner is involved through an inference engine, e.g. the Jess engine involves a Pellet reasoner.
W3 (World wide web consortium) has published a list of reasoners [1]
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
Examples of reasoners
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
FaCT++ is an open-source tableaux-based OWL 2 DL reasoner. It is implemented in C++ and shows exceptional performance on expressive ontologies.
- Fully conformant with OWL DL except for keys and some datatypes
- new developed based on ideas from FaCT
HermiT can determine whether or not the input ontology is consistent, identify subsumption relationships between classes, and much more.
- Based on a novel hypertableau algorithm,
- efficient reasoning
- Fully conformant
Pellet is an open-source Java OWL DL reasoner
- developed by
- tableau based decision procedure
Jena is an open source framework, including reasoning modules
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
Terminology
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
Assertional Box (Abox)
- contains assertions about individuals,i.e. OWL facts such as type, property-value...
- Realizing the ABox, i.e. computing the most specific concept(s) that each individual is an instance of.
- Example: all people being students
Terminological Box (Tbox)
- contains axioms about classes, i.e.OWL axioms such as subclass, equivalent class...
- Example: 'Class:Pizza has subclass:American Pizza'
Knowledge Base (KB):
- A combination of an ABox and a TBox, i.e.a complete OWL ontology.
major use cases:
- Frequent ABox changes (situation classification) and
- rare ABox changes (social networks).
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
Reasoner comparison
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
Good intro from Bock et al.[2]
- open source versus other licenses
- language, portability
- logic support (e.g. OWL DL)
- performance:
- load time
- query time
- addressing: Language complexity, and size of ontology
Conclusions from Bock et al.
- reasoners that employ a simple rule engine scale very well for large ABoxes, but are in principle very limited to lightweight language fragments,
- classical tableau reasoners scale well for complex TBox reasoning tasks, but are limited with respect to their support for large ABoxes,
- the reasoning techniques based on reduction to disjunctive datalog as implemented in KAON2 scale well for large ABoxes, while at the same time they support are rich language fragment.
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
Pellet
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
based on a presentation by Susana: Media:Pellet_Reasoner.pdf
- Pellet is an open-source Java based OWL DL reasoner, see Pellets-based_reasoning
- can be used with Jena and OWL API libraries.
Features:
- Consistency checking: ensures that an ontology does not contain any contradictory facts.
- Concept satisfiability: checks if it is possible for a class to have any instances.
- Classification: computes the subclass relations between every named class to create the complete class hierarchy.
- Realization: computes the direct types for each of the individuals.
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
Main modules
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
- Parsing and Loading: Pellet include different submodules that can load ontologies from different representations (Jena, WonderWeb..).
- Tableaux Reasoner: has the functionality of checking the consistency of an ontology by constructing a graph from the Abox.
- class relations: subsumption, satisfiability, and classification
- Datatype Reasoner: is responsible for checking if the intersection of datatypes is consistent or not.
- Knowledge Base Interface: makes decisions to check the consistency of the ABox, when to classify all the concepts or when to realize all the individuals and answer queries.
- ABox Query Engine for retrieval, conjunctive query answering
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
Reasoner outcome
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
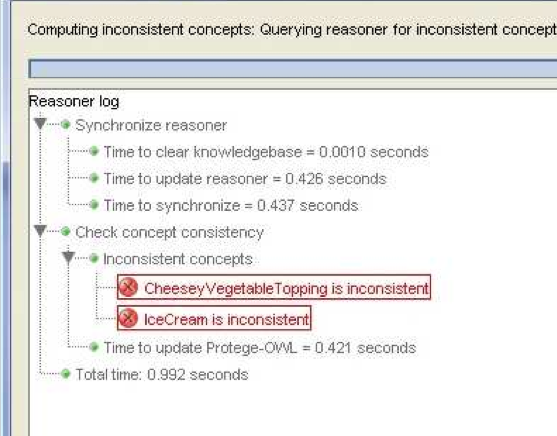
Reasoners detect inconsistent ontologies but the diagnosis and resolution of the bug is not supported at all.
- Pellet contains two debugging services that help explain why the inconsistency occurs:
- service clash detection is used to pinpoint the root contradiction or clash in the completion graph;
- axiom tracing is used to extract the relevant source axioms from the ontology responsible for the clash.
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
Discussion
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found
- internal consistency check versus external rules
- implementation of external rules
- Example: Jess Engine in Protege 3.x
- Example: Rule tab in Protege 4.x
- Rules are not limited to SWRL define your own "custom built-ins"
- reference: Custom SWRL
Cite error: <ref> tags exist, but no <references/> tag was found