Courses and Knowledge
| Wiki for ITS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Contents
Knowledge management through collaborative platforms
This page describes how knowledge management can be fostered through collaborative platforms. It takes aspects of people, their activities and establishes knowledge based on activities.
Goal
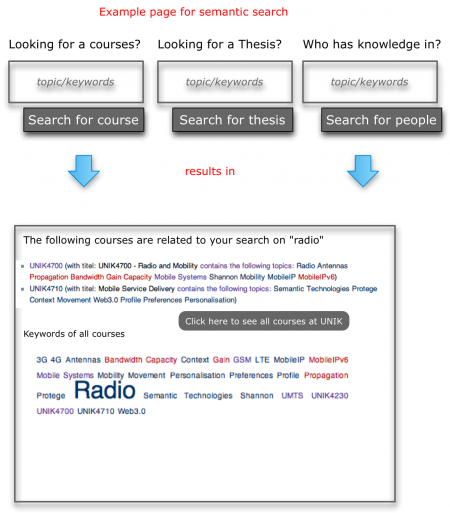
The goal of the knowledge platform is to provide an easy entry points for visitors and users, to find valuable information on the topics they are looking for. This includes:
- Students looking for courses related to a certain topic.
- Collaboration partners searching for a master thesis in a certain area
- Visitors searching for people with expertise in a certain area.
Our vision
Our vision is to use the Web as an interactive platform for the knowledge representation. While knowledge can be aggregated by following the activities of the user, structured knowledge can be achieved through the use of semantic technologies.
Our approach is to use keywords as the easiest entry point for information. "Regardless" of whatever you are doing, some keywords are provided. These keywords will then be placed in relation to each other. When the keyboard base is mapped sufficiently, it will represent the knowledge in the organisation.
Through using semantics we also ensure the interoperability between different systems. The annotated information can simply be imported and exported, e.g. "export all info changed today".
Courses
Courses are subdivided in lectures. We assume that a lecturer has the knowledge on the lecture he is giving. Thus, providing keywords to lectures will mean that these topics (tags) will also apply for the lecturer.
One might extend that to students joining courses, though providing them with "reduced height" of the tags.
Thesis
Master and PhD thesis work has always supervisors. Usually it is assumed that a PhD student knows more than his supervisor. The main supervisor might be an expert in the area, whereas co-supervisors only cover a certain area...
Thesis supervision can thus be used for providing indications of knowledge.
Notes
Companies working with similar ideas:
- xxx ask Kaosher for the tool being used in NSN
Programs used elsewhere
- UiO har inngått avtale med MOOC plattformen FutureLearn
Video Tools
Tool of editing and procesing videos:
and a screen recorder (with this one you can capture your screen and your voice).
- http://www.techsmith.com/camtasia.html (for mac)
- http://www.screenr.com/
- An example: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VqsyTbFLbxU
Moodle
Moodle http://demo.moodle.net/ has been successfully used in two Spanish universities:
Fronter
the platform has a virtual whiteboard which can be a solution about recording a writing without camera.
- http://www.elluminate.com/downloads/whitepapers/Elluminate_PowerLink_for_Blackboard_Learning_Management_System_CE_and_Vista.pdf
- An example: https://sas.elluminate.com/site/external/jwsdetect/playback.jnlp?psid=2011-04-21.1237.M.C28E1B31E47F0CBF5A595CF03E6276.vcr&sid=2010107
Cousera, edX and Udacity
- Coursera has one option called "signature track": for earn official recognition, link the student profile to their real identity (using Photo ID and typing pattern) for security access and code of conduct.
- Coursera and edX have the options register/unregister; but Udacity have not the option for unregister.
- See http://ResearchKjeller.no for challenges in collaboration
Related learning initiatives
MatRIC - The Centre for Research, Innovation and Coordination of Mathematics Teaching (MatRIC) is a centre of excellence that works with digital assessment, simulations, video tutorials, live streaming of mathematics lectures and plans to develop a video library for teaching and learning mathematics. MatRIC aims at enhancing the students ́experiences of learning mathematics.
DELP - The Distance Education Leapfrogging Project (DELP) is a five years (2013 - 2018) project to enhance ICT pedagogical integration and increase access to education in Africa. In collaboration with Makerere University (Uganda), UiA provides technical expertise in modern teaching methods using digital media technology. This comprises of staff training at postdoctoral and PhD level, creation of new blended learning programmes at Bachelor and Master level as well as infrastructure development. The main goal is to increase Makerere University ́s capacity to offer 4th and 5th generation distance education.
ADILA - The Agder Digital Learning Arena (ADILA) is a four years (2014 - 2018) strategic research project in the area of future learning. The focus is on new modes of teaching and learning on campus, distance education, blended learning, assessment, the use of virtual resources (virtual labs, virtual microscopes, etc.), uses of social media in education, etc. The work packages (4 PhD projects) include investigations on innovations in teaching and learning using digital assessments; formative assessment of mathematics learning; collaborative learning through digital media and the transformation of education.
A-PASS - The Agder Peer Assessment (A-PASS) is an innovative research project to use mobile technology based tools for collaborative learning. Starting in 2010, the project has investigated how students can be more involved into learning mathematics through assessing each other’s work. A novel mobile tablet based solution was designed to support the assessment for learning. The research work contributed to the difficult task of assessing mathematics in order to provide high quality feedback to many students, and engaging them more into learning. The major findings of A-PASS were published as a PhD dissertation and further investigations are being carried out.
eUNIK - Electronic teaching has been at the heart of UNIK's work from the start, and were related to the Internet development taking place at Kjeller. The Arpanet got its first European connection in the UNIKs building in June 1973. Both Telenor Research and Development and Opera Software were founded at Kjeller. UNIK has established 70% of all lecture rooms with video and smartboard facitilites, allowing distance education of everyone. The majority of lectures are streamed, and students can join with their own equipment or through electronic classrooms at the CWI premises in Norway. Research and Education collaboration is established between all CWI partners, allowing students to select topics of their choice.
DragonBox Algebra, developed by WeWantToKnow and which proves that maths can be learned much more efficiently, has been internationally recognized as one of the best serious games ever, receiving awards all around the world, and prompting researchers to further study the benefits of this amazing new resource. DragonBox is subject to ongoing research and testing by the Center for Game Science at the University of Washington. This research is being used to refine our current products and develop future products. In the same way, WWTK is working in new learning tools and they are looking and covering the full math curriculum and will change the way kids learn.