Difference between revisions of "Nextelco:Application Server"
(→Application Server) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
* [[Nextelco:DHCP|DHCP server]]: provides different range IP addresses depending on the requesting device. | * [[Nextelco:DHCP|DHCP server]]: provides different range IP addresses depending on the requesting device. | ||
* [[Nextelco:DNS|DNS server]]: provides easy to remember names for devices which compose the service network. Specially interesting for device management and maintenance. | * [[Nextelco:DNS|DNS server]]: provides easy to remember names for devices which compose the service network. Specially interesting for device management and maintenance. | ||
| + | * [[Nextelco:Web|Web server]]: this service will provide the necessary interface to deal with the voucher system. | ||
| + | * [[Nextelco:DB|DB server]]: data base service is necessary to keep all accounting information in a centralized place and access it whatever the service we are using to manage users. | ||
* [[Nextelco:Management|Management server]]: composed by Network Management System (NMS) for Radio Access Network (RAN) and RCMS for Base Station (BS) view and configuration. | * [[Nextelco:Management|Management server]]: composed by Network Management System (NMS) for Radio Access Network (RAN) and RCMS for Base Station (BS) view and configuration. | ||
* [[Nextelco:Maintenance|Maintenance server]]: different and necessary services for network maintenance such as TFTP, SYSLOG, Time service (NTP), Speed test and File sharing. | * [[Nextelco:Maintenance|Maintenance server]]: different and necessary services for network maintenance such as TFTP, SYSLOG, Time service (NTP), Speed test and File sharing. | ||
The Application Server could be one or a combination of several physical servers. Each server could hold just one machine or a combination of different virtual machines. This will be decided depending on physical servers availability as well as their resources. | The Application Server could be one or a combination of several physical servers. Each server could hold just one machine or a combination of different virtual machines. This will be decided depending on physical servers availability as well as their resources. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == System installation == | ||
| + | The application server has the following hardware characteristics: | ||
| + | * Intel Xeon 3.2GHz x 4 | ||
| + | * 4GB RAM | ||
| + | * Three network interfaces | ||
| + | ** Two Ethernet copper | ||
| + | ** One fiber | ||
| + | * Two 36GB identical hard drives | ||
| + | |||
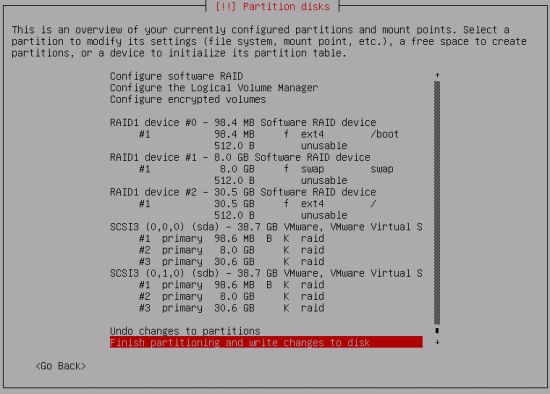
| + | Regarding the software, it is based on Debian GNU/Linux 7.5 (wheezy) distribution. Due to fact that the server has two equal hard drives, during Debian installation software based RAID1 has been set up. These are the partitions: | ||
| + | *1 -> 100MB /boot | ||
| + | *2 -> 8 GB swap | ||
| + | *3 -> Rest / | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Nextelco_appserver_raid.png|550px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The configuration of RAID1 has been done according to this web page [http://www.iprobot.net/linux-tutorial/how-to-setup-software-raid-in-debian-ubuntu/ RAID on debian.] | ||
| + | However there are more useful web pages: | ||
| + | *[http://feeding.cloud.geek.nz/posts/setting-up-raid-on-existing/ Setting up RAID] | ||
| + | *[http://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/25513/is-grub-installed-to-all-the-mbr-of-a-raid-array-by-default-by-the-debian-instal GRUB on RAID] | ||
| + | After Debian installation it is important to set up GRUB on both hard drives. To do that this is the command that has been used: | ||
| + | #dpkg-reconfigure -plow grub-pc | ||
| + | Additionally, if we want to check RAID status we use this command: | ||
| + | #cat /proc/mdstat | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is convenient to install a SSH server in order to access the server remotely for any reason. These are the steps followed to install the SSH server: | ||
| + | <ol> | ||
| + | <li>Install openssh-server together with blacklisted RSA and DSA keys</li> | ||
| + | #apt-get install openssh-server openssh-blacklist openssh-blacklist-extra | ||
| + | <li>It is convenient to set up shared keys based log in. This increases the security level together with the deny of root login and password-based authentication. </li> | ||
| + | <ol> | ||
| + | <li>Generate in the local machine a RSA key pair.</li> | ||
| + | $ssh-keygen -t rsa | ||
| + | <li>Copy on the server the generated public key.</li> | ||
| + | $scp path_to_RSA_key username@server:/home/username/.ssh/authorized_keys | ||
| + | <li>Edit openssh-server configuration</li> | ||
| + | #vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config | ||
| + | -- change | ||
| + | #AuthorizedKeysFile %h/.ssh/authorized_keys | ||
| + | -- to | ||
| + | AuthorizedKeysFile %h/.ssh/authorized_keys | ||
| + | -- change: | ||
| + | #PasswordAuthentication yes | ||
| + | -- to | ||
| + | PasswordAuthentication no | ||
| + | -- change | ||
| + | PermitRootLogin yes | ||
| + | -- to | ||
| + | PermitRootLogin no | ||
| + | <li>Restart sshd server</li> | ||
| + | #invoke-rc.d ssh restart | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
| + | <li>In order to access the server through SSH this is the necessary command.</li> | ||
| + | $ssh -i path_to_id_rsa(private) username@server | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
| + | |||
Return to [[Nextelco:Technology|Technology]] page. | Return to [[Nextelco:Technology|Technology]] page. | ||
Latest revision as of 16:24, 5 July 2014
Application Server
The application server is a combination of different services which are necessary for the management of user accounts and devices which provide connectivity to end-users. This are the services offered by the application server:
- AAA server: provides end-users and devices Authentication, Authorization and Accounting.
- Billing server:
- DHCP server: provides different range IP addresses depending on the requesting device.
- DNS server: provides easy to remember names for devices which compose the service network. Specially interesting for device management and maintenance.
- Web server: this service will provide the necessary interface to deal with the voucher system.
- DB server: data base service is necessary to keep all accounting information in a centralized place and access it whatever the service we are using to manage users.
- Management server: composed by Network Management System (NMS) for Radio Access Network (RAN) and RCMS for Base Station (BS) view and configuration.
- Maintenance server: different and necessary services for network maintenance such as TFTP, SYSLOG, Time service (NTP), Speed test and File sharing.
The Application Server could be one or a combination of several physical servers. Each server could hold just one machine or a combination of different virtual machines. This will be decided depending on physical servers availability as well as their resources.
System installation
The application server has the following hardware characteristics:
- Intel Xeon 3.2GHz x 4
- 4GB RAM
- Three network interfaces
- Two Ethernet copper
- One fiber
- Two 36GB identical hard drives
Regarding the software, it is based on Debian GNU/Linux 7.5 (wheezy) distribution. Due to fact that the server has two equal hard drives, during Debian installation software based RAID1 has been set up. These are the partitions:
- 1 -> 100MB /boot
- 2 -> 8 GB swap
- 3 -> Rest /
The configuration of RAID1 has been done according to this web page RAID on debian.
However there are more useful web pages:
After Debian installation it is important to set up GRUB on both hard drives. To do that this is the command that has been used:
#dpkg-reconfigure -plow grub-pc
Additionally, if we want to check RAID status we use this command:
#cat /proc/mdstat
It is convenient to install a SSH server in order to access the server remotely for any reason. These are the steps followed to install the SSH server:
- Install openssh-server together with blacklisted RSA and DSA keys
- It is convenient to set up shared keys based log in. This increases the security level together with the deny of root login and password-based authentication.
- Generate in the local machine a RSA key pair.
- Copy on the server the generated public key.
- Edit openssh-server configuration
- Restart sshd server
- In order to access the server through SSH this is the necessary command.
#apt-get install openssh-server openssh-blacklist openssh-blacklist-extra
$ssh-keygen -t rsa
$scp path_to_RSA_key username@server:/home/username/.ssh/authorized_keys
#vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config -- change #AuthorizedKeysFile %h/.ssh/authorized_keys -- to AuthorizedKeysFile %h/.ssh/authorized_keys -- change: #PasswordAuthentication yes -- to PasswordAuthentication no -- change PermitRootLogin yes -- to PermitRootLogin no
#invoke-rc.d ssh restart
$ssh -i path_to_id_rsa(private) username@server
Return to Technology page.