UNIK4710/UNIK9710 Introduction
Josef Noll, Susana Rodriguez de Novoa,
Overview UNIK4710, UNIK9710
Mobile Semantic Service Delivery
- first lecture
- sign up to cwi.unik.no Signup
- confirm your email
- add yourself to UNIK4710V14Participants
- what do you expect
- discuss
- tell
- Goal of the course,
- what to achieve
- how to achieve it
- Examen
- what to I expect
What to achieve
Academic work
- how we build up list of references
- modelling approach
- detailed list of topic (next slide)
Develop an own-standing example of context-awareness
- think about a scenario
- present the scenario
- identify the categories which need semantics (=machine readable understanding of context)
- implement an ontology (= hierarchical representation of information)
- establish rules to reason (= retrieve information) from the data
Examen
- Presentation of research topic (mandatory), home work on comparison of selected topics (60 %) and simulation work (40 %).
- The student may ask for an oral exam in which case the home work on comparison of selected topics counts 50%, the simulation work 30% and the oral exam 20%.
Mandatory
- knowledge of presentation material - "how you presented"
- presentation and analysis of 3-4 papers
- programming of user, context....
Evaluation
Expections for your presentation
- Define what to present
- Present it such that your colleagues can understand
- Facts/Reference-based presentation
- Evaluate your own work
- Checklist
- relevant for the course
- understandable
- your own evaluation
- scientific: "Don't guess, present references"
Meeting calendar
- will be published through this wiki: http://cwi.unik.no/wiki/UNIK4710
- see what we had done in earlier years 2012 lecture list
based on
- your topics
- the goal we want to achieve
What are you going to learn
- Collect publications for personalised service and context-aware services.
- Identify the key-features of personalised and context-aware services
- Tabulate the requirements for such services
- Describe the difference between an Internet service, a mobile service and a proximity service
- Present specific knowledge based on collected publications
- Identify semantic technologies for description of the user and his context
- Describe the difference between ontologies and rules
- Establish interworking of ontologies created by members of the course
- Construct rules to define the context of the user
- Apply rules on top of ontologies to enhance knowledge
- Produce examples of context-aware services
- Evaluate the functionality of context-aware service examples
- Program interfaces to exteral knowledge
- Generate a simply application demonstrating context-awareness
Mobile Semantics
What makes mobile communications so difficult?
- know principle numbers of "round-trip delay" in mobile and wireless systems
- know the principles of e.g. UDP, TCP
- can explain how these hang together
Notes:
- Media:Introduction_to_TCP.pdf - Introduction to TCP from Thomas (?) Master Thesis
Discussion
- these are my wishes
- what do you expect?
- what are the top three wishes for the course?
5 min discussion 2 x 2 - write down
Methodology
Suggestion:
- select references
- explain and discuss papers
- critics, alternatives, ...
What would you like to see?
Tasks for two weeks
- n.n. discussion on a mobile scenario
- n.n. presentation on "context"
List of references, provide 3-5 references on
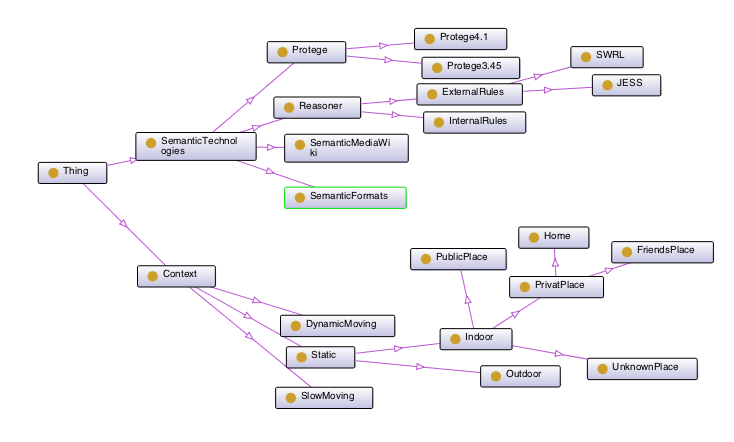
Keywords in Mobile Semantics
- ontology
- user profiles, identities, roles
- community profiles
- context profiles
- semantic rules
- reasoning
Generate "introduction to protege"
- difference protege 4 versus protege 3.x
- what to know
- Rules for semantic - implementations
TOC - overview Mobile Semantics
- Basics of Semantics
- Mobile Challenges
- Identity, roles
Programming
- Introduction Protégé
- Programming User/Community Profile
- Semantic Rules
TOC - Rules and Context
Studies
- Semantic rules
- Challenges Semantic Access
- Context awareness
Programming
- Context and user profile, semantic rules to decide which content to release
- Context Ontology and Reasoning
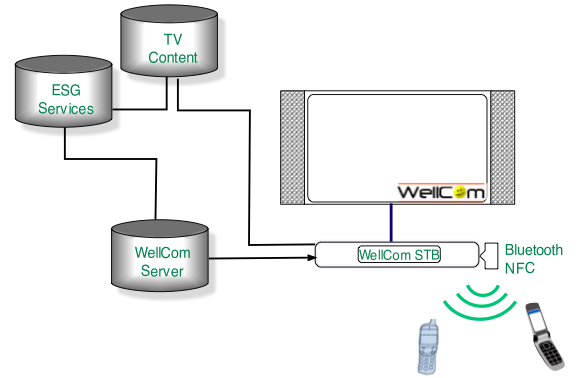
Example: Context Aware and Personalised
Architecture components (3)
Achieved through
- User authentication
- User is authenticated through Bluetooth
- Personal content
- Video, Audio and Pictures from Bob are presented
- Content filtering
- Preferred Content filtered from ESG is shown
- see YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y9tdrAzJgac
Summary
- Mobile Semantics handles a formalised description of context-aware services in a mobile scenario