Difference between revisions of "A4-Signal Strength and Capacity"
Josef.Noll (Talk | contribs) m (Josef.Noll moved page A4 to A4-Signal Strength and Capacity) |
Josef.Noll (Talk | contribs) (→⌘ Shannon - examples) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
== Comments== | == Comments== | ||
| − | [[File:F3-3.png|500px | + | [[File:F3-3.png|500px]] |
| + | |||
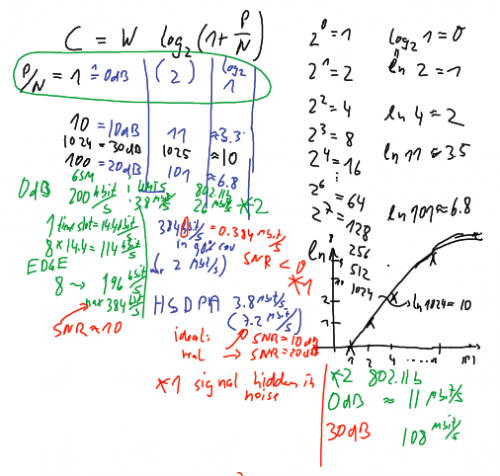
Figure: ''Calculation'' of Shannon capacity for GSM (GPRS, EDGE), UMTS (packet data, HSDPA) and 802.11b | Figure: ''Calculation'' of Shannon capacity for GSM (GPRS, EDGE), UMTS (packet data, HSDPA) and 802.11b | ||
| − | [[File:F3-4.png|450px | + | [[File:F3-4.png|450px] |
| + | |||
Figure: Log_10 funtion and related power. The power expressed in dB is 10 times the log_10 of the normalised power. | Figure: Log_10 funtion and related power. The power expressed in dB is 10 times the log_10 of the normalised power. | ||
There are also the abbreviations | There are also the abbreviations | ||
* <math>dB_m</math> stands for power with respect to 1 mW. <span style="color:#000B80">How much is 0 dB_m and 10 dB_m? | * <math>dB_m</math> stands for power with respect to 1 mW. <span style="color:#000B80">How much is 0 dB_m and 10 dB_m? | ||
| − | * <math>dB_a</math> Power of a sound (or music). | + | * <math>dB_a</math> Power of a sound (or music). |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
=⌘ Cell capacity in UMTS = | =⌘ Cell capacity in UMTS = | ||
Revision as of 16:35, 21 September 2014
| Wiki for ITS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Contents
⌘ A4-Signal Strength and Capacity
Main focus in the previous lectures was on propagation effects. We will first repeat the main conclusions from last lecture on electromagnetic signals, and then introduce the capacity of a system based on Shannon's theorem.
New literature:
- J. Noll, K. Baltzersen, A. Meiling, F. Paint , K. Passoja, B. H. Pedersen, M. Pettersen, S. Svaet, F. Aanvik, G. O. Lauritzen. '3rd generation access network considerations'. selected pages from Unik/FoU R 3/99, Jan 1999 (.pdf]])
- H. Holma, A. Toskala (eds.), "WCDMA for UMTS", John Wiley & sons, Oct 2000, selected pages
Comments
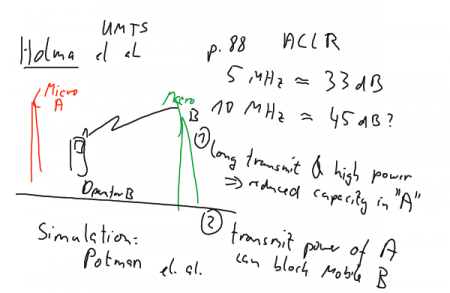
Figure: Illustrating reduction of capacity in network A (top) and blinding of phones in cell (B)
More detailed discussions on these effects can be found in the literature indicated above.
⌘ Signal/noise ratio
,
where P is average power
- why talking about noise?
- dB,
- near-far problem
[source: Wikipedia]
⌘ Shannon Theorem
- The fundamental theorem of information theory, or just Shannon's theorem, was first presented by Claude Shannon in 1948.
- Given a noisy channel with channel capacity C and information transmitted at a rate R, then if R < C there exist codes that allow the probability of error at the receiver to be made arbitrarily small. This means that theoretically, it is possible to transmit information nearly without error at any rate below a limiting rate, C.
- See File:LarsLundheim-Telektronikk2002.pdf: The channel capacity of a band-limited information transmission channel with additive white, Gaussian noise. This capacity is given by an expression often known as “Shannon’s formula”:
[bits/s]
with W as system bandwidth, and in case of interference free environment, otherwise
, where
with
as Boltzmann constant and
as temperature in Kelvin.
Exercises:
- If the SNR is 20 dB, and the bandwidth available is 4 kHz, what is the capacity of the channel?
- If it is required to transmit at 50 kbit/s, and a bandwidth of 1 MHz is used, what is the minimum S/N required for the transmission?
[source: Wikipedia, Telektronikk 2002]
⌘ Shannon - examples
[bits/s]
Examples
- calculate capacity for W= 200 kHz, 3.8 Unik/MHz, 26 Unik/MHz, (all cases P/N = 0 dB, 10 dB, 20 dB)
Comments
Figure: Calculation of Shannon capacity for GSM (GPRS, EDGE), UMTS (packet data, HSDPA) and 802.11b
[[File:F3-4.png|450px]
Figure: Log_10 funtion and related power. The power expressed in dB is 10 times the log_10 of the normalised power.
There are also the abbreviations
-
stands for power with respect to 1 mW. How much is 0 dB_m and 10 dB_m?
-
Power of a sound (or music).
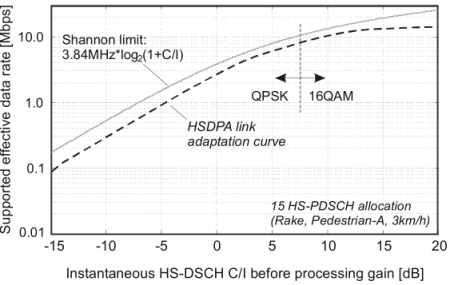
⌘ Cell capacity in UMTS
UMTS has good efficiency with respect to Shannon
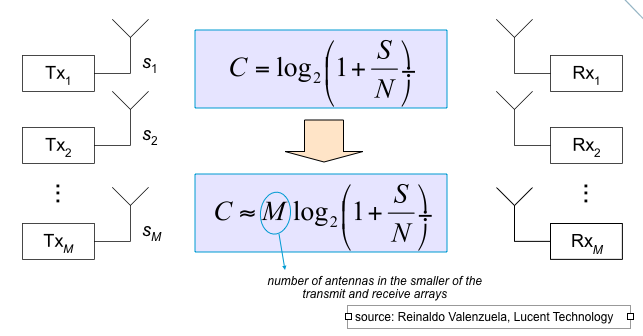
⌘Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output: MIMO
Figure: using multiple wave propagation in a MIMO system
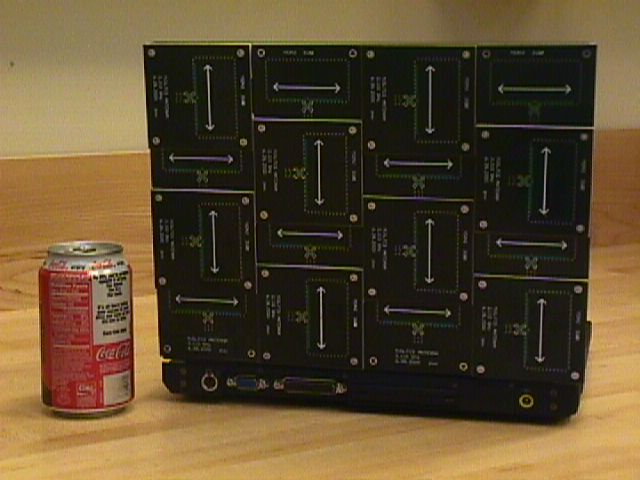
⌘MIMO laptop
Figure: A MIMO equipped laptop (Source:Valenzuela, BLAST project)
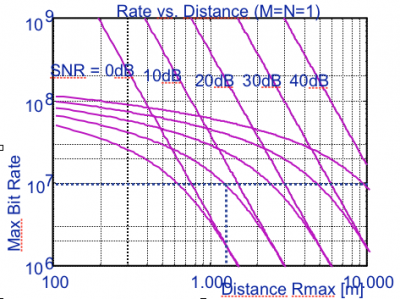
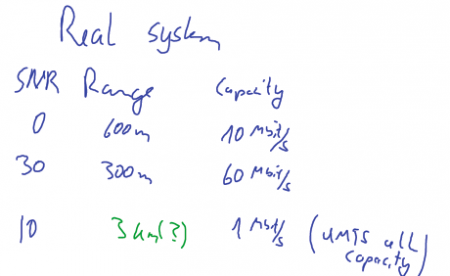
⌘ Range versus SNR
|
[Source:Valenzuela, BLAST project] |
Lessions learned
Let's start What have we learned?
- antenna characteristics and gain
- what happens if I double the frequency (900 - 1800 - 2400 MHz)?
- minimum GSM receiver sensitivity
- other questions related to radio?
Comments
Range
[Source Valenzuela, BLAST project]
why is there no relation to frequency?
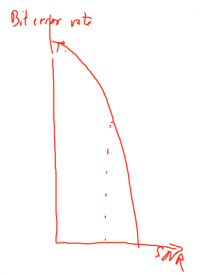
Relation of Bit Error Rate and SNR