Difference between revisions of "IoTSec:T1.2"
From its-wiki.no
Josef.Noll (Talk | contribs) |
Josef.Noll (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
|Lead partner=UNIK | |Lead partner=UNIK | ||
|Partner=UNIK, NR, Ifi, | |Partner=UNIK, NR, Ifi, | ||
| − | |Objective=This task will establish the Multi-Metrics Model for the Smart Grid use case | + | |Objective=This task will establish the Multi-Metrics Model for the Smart Grid use case. The task includes |
| − | * | + | * the adaptation to the real world infrastructure |
| + | * the analysis of the most relevant sub-systems | ||
| + | * application specific goals for security, privacy and dependability | ||
}} | }} | ||
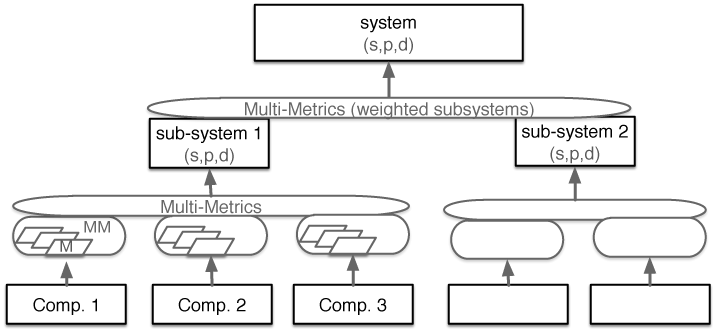
| − | The Multi-Metrics Approach has the goal to | + | The Multi-Metrics Approach has the goal to to measure the Security, Privacy and Dependability (SPD) level of a system. The objective is to achieve an overall system SPD level, SPD<sub>System</sub>. The main advantage of this methodology is that it provides a simple mechanism to measure and evaluate the system security, privacy and dependability levels. |
| + | |||
| + | SPD<sub>System</sub> is a triplet, composed of individual Security, Privacy and Dependability levels (s,p,d). Each of the levels is represented by a range be- tween 0 and 100, i.e. the higher the number, the higher the Security, Privacy and Dependability level. However, in order to end up with SPDSystem, during the whole process, the criticality is evaluated. Criticality is again a triplet (Cs,Cp,Cd), defined as the complement of SPD, and expressed as (Cs, Cp, Cd) = (100, 100, 100) − (s, p, d). | ||
| + | |||
[[File:MultiMetrics_System.gif]] | [[File:MultiMetrics_System.gif]] | ||
| + | The Figure shows a system being composed of multiple sub-systems, which at the same time consist of various components. | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Challenges = | ||
| + | Identified challenges are related to | ||
| + | * industrial harmonisation of methodology | ||
| + | * semantic description of security, privacy and dependability | ||
| + | * identification of spd values for use case, e.g. monitoring, alarm, control | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Expected outcome = | ||
| + | Y1: | ||
| + | * System analysis for main sub-systems, | ||
| + | * identification of 3-5 use cases, | ||
| + | * security analysis for 1 use case, | ||
| + | * discussion with industry | ||
| + | |||
| + | Y2: | ||
| + | * goal and system analysis for at least 4 use cases, | ||
| + | * identification of challenges | ||
| + | |||
| + | Y3: | ||
| − | = | + | =References = |
# J. Noll, I. Garitano, S. Fayyad, E. Åsberg, H. Abie, «Measurable Security, Privacy and Dependability in Smart Grids», Journal of Cyber Security, 3_4, (2015) | # J. Noll, I. Garitano, S. Fayyad, E. Åsberg, H. Abie, «Measurable Security, Privacy and Dependability in Smart Grids», Journal of Cyber Security, 3_4, (2015) | ||
# I. Garitano, S. Fayyad, J. Noll, «Multi-Metrics Approach for Security, Privacy and Dependability in Embedded Systems», Wireless Pers. Commun. 81, pp1359-1376 (2015) | # I. Garitano, S. Fayyad, J. Noll, «Multi-Metrics Approach for Security, Privacy and Dependability in Embedded Systems», Wireless Pers. Commun. 81, pp1359-1376 (2015) | ||
Revision as of 20:53, 14 August 2015
| Security in IoT for Smart Grids | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
T1.2 Measurable Security
| Task Title | Measurable: security, privacy and dependability, metrics |
|---|---|
| WP | IoTSec:WP1 |
| Lead partner | UNIK |
| Leader | |
| Contributors | UNIK, NR, Ifi |
| edit this task |
Objective
This task will establish the Multi-Metrics Model for the Smart Grid use case. The task includes
- the adaptation to the real world infrastructure
- the analysis of the most relevant sub-systems
- application specific goals for security, privacy and dependability
| Category:Task |
Deliverables in T1.2 Measurable Security
| Title | Due month | Lead partner | Editor | Dissemination level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1.2.1 | Methods for measurable security (draft) | M12 | ITS | Josef Noll | Public |
| D1.2.2 | Methods for measurable security (final) | M24 | ITS | Josef Noll | Public |
The Multi-Metrics Approach has the goal to to measure the Security, Privacy and Dependability (SPD) level of a system. The objective is to achieve an overall system SPD level, SPDSystem. The main advantage of this methodology is that it provides a simple mechanism to measure and evaluate the system security, privacy and dependability levels.
SPDSystem is a triplet, composed of individual Security, Privacy and Dependability levels (s,p,d). Each of the levels is represented by a range be- tween 0 and 100, i.e. the higher the number, the higher the Security, Privacy and Dependability level. However, in order to end up with SPDSystem, during the whole process, the criticality is evaluated. Criticality is again a triplet (Cs,Cp,Cd), defined as the complement of SPD, and expressed as (Cs, Cp, Cd) = (100, 100, 100) − (s, p, d).
The Figure shows a system being composed of multiple sub-systems, which at the same time consist of various components.
Challenges
Identified challenges are related to
- industrial harmonisation of methodology
- semantic description of security, privacy and dependability
- identification of spd values for use case, e.g. monitoring, alarm, control
Expected outcome
Y1:
- System analysis for main sub-systems,
- identification of 3-5 use cases,
- security analysis for 1 use case,
- discussion with industry
Y2:
- goal and system analysis for at least 4 use cases,
- identification of challenges
Y3:
References
- J. Noll, I. Garitano, S. Fayyad, E. Åsberg, H. Abie, «Measurable Security, Privacy and Dependability in Smart Grids», Journal of Cyber Security, 3_4, (2015)
- I. Garitano, S. Fayyad, J. Noll, «Multi-Metrics Approach for Security, Privacy and Dependability in Embedded Systems», Wireless Pers. Commun. 81, pp1359-1376 (2015)