Difference between revisions of "B4-Attenuation and Scattering"
From its-wiki.no
Josef.Noll (Talk | contribs) (→⌘ Path loss calculation) |
Josef.Noll (Talk | contribs) (→⌘ Path loss calculation) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
== ⌘ Path loss calculation == | == ⌘ Path loss calculation == | ||
[[File:TableWirelessISM.png|400px|right]] | [[File:TableWirelessISM.png|400px|right]] | ||
| − | Hydra pass loss approximation | + | Hydra pass loss approximation<br/> |
| − | <math> L = 92,4 + 20 \log(d \mathrm{[km]}) + 20 \log(f \mathrm{[GHz]}) + \sum{n_i \alpha_i}</math> | + | <span style="font-size: 140%;"><math> L = 92,4 + 20 \log(d \mathrm{[km]}) + 20 \log(f \mathrm{[GHz]}) + \sum{n_i \alpha_i}</math></span> |
* <span style="color:#000B80">relation between fading margin and receiver sensitivity</span> | * <span style="color:#000B80">relation between fading margin and receiver sensitivity</span> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:20, 26 September 2017
| Wiki for ITS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Contents
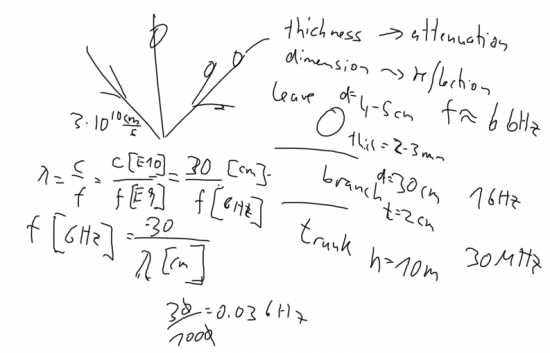
⌘ Interaction of electromagnetic waves with the Environment
Examples are:
- leaves will mainly interact around 6 Unik/GHz: thickness will attenuate, whereas reflection is due to diameter of leaves
- branches will have main interaction at about 1 Unik/GHz
- the tree trunk will interact with almost all frequencies at 30 Unik/MHz and above.
⌘ Attenuation in walls
| Attenuation in material follows typical an exponential behaviour. | 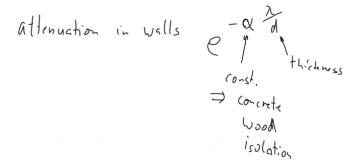
|
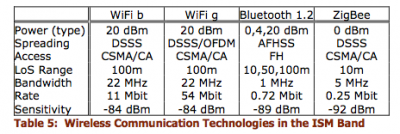
⌘Attenuation parameters for 2.4 GHz
| Obstacle | Attenuation |
|
|---|---|---|
| Brick wall with window | 2 | |
| Brick wall next to metal door | 3 | |
| Cinder Block wall | 4 | |
| Office wall | 6 | |
| Metal door in office wall | 6 | |
| Metall door in brick wall | 12.4 | |
| Floor | 30 |
Measurements performed for European building
(Source:Hydra Deliverable D5.4, p 12)
⌘ Path loss calculation
Hydra pass loss approximation
- relation between fading margin and receiver sensitivity