Difference between revisions of "D4-Mobile Systems"
Josef.Noll (Talk | contribs) |
Josef.Noll (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<span scaled="60%>[Presentation G. Fettweis, IEEE VTC forum Baltimore], http://www.ieeevtc.org/plenaries/vtc2007fall/28.pdf </span> | <span scaled="60%>[Presentation G. Fettweis, IEEE VTC forum Baltimore], http://www.ieeevtc.org/plenaries/vtc2007fall/28.pdf </span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == ⌘Example of propagation == | ||
| + | Results for UMTS (''worst case''), with 3 sector antenna | ||
| + | * Range of unloaded cell is 700 m in urban pedestrian | ||
| + | * With loaded cell, assumed increase of noise by 10 dB, max cell radius 390 m | ||
| + | * vehicular with typical range of 3600 m (unloaded) and 1900 m (loaded) | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Next: examples and simulations | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == ⌘Oslo simulations, performed for GSM at 1800 MHz == | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | [[File:Oslocov25dBm.jpg|400px|Transmission at 25 dBm]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | [[File:Oslocov35dBm.jpg|400px|Transmission at 35 dBm]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:scaleimage.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="color:#000B80">how much does the range decrease when reducing the power by 10 dB? | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | (Source: Helge Dommarsnes, Telenor Mobil) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == ⌘Difference GSM - UMTS == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Q16parameterGSM.png|450px|right|Illustration of Q_16 parameter in GSM]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Frequency | ||
| + | * Receiver structure | ||
| + | ** GSM sliding window of 16 <math>\fs3 \mu s</math> | ||
| + | ** UMTS Rake receiver | ||
| + | |||
| + | Q16ratio:The ratio of the power inside to the power outside a window of duration 16 <math>\fs3 \mu s</math>. For each IR the window is slid to find the position with highest power inside the window. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | (Source:R Rækken, G. Løvnes, Telektronikk) | ||
| + | |||
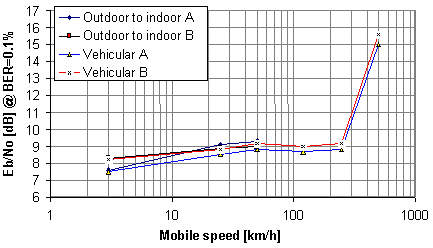
| + | == ⌘Results of link level simulation == | ||
| + | [[File:LinkLevelEBN0.png|500px|right]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Simulations to achieve minimum W-CDMA using given QoS parameter: here voice service | ||
| + | |||
| + | (Source: Eurescom P921, D2) | ||
| + | |||
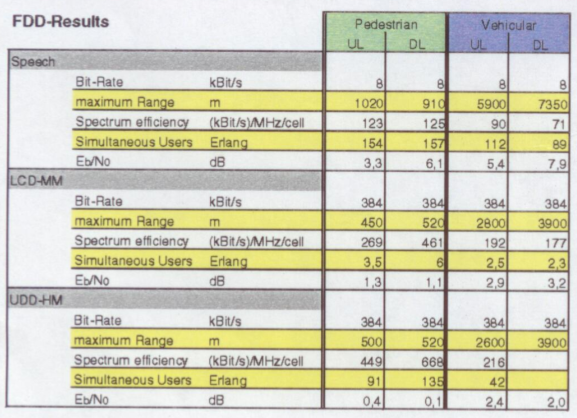
| + | == ⌘UMTS traffic simulations== | ||
| + | [[File:FDD-results.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | (Source:Telenor FoU report 3-99) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
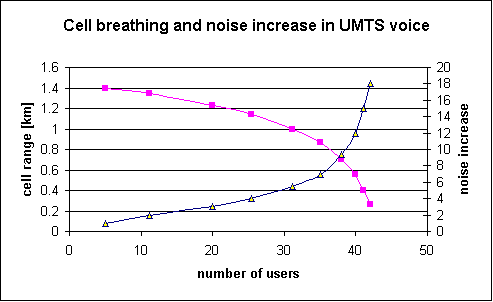
| + | == ⌘Cell Breathing effect in UMTS== | ||
| + | [[File:CellBreathing-UMTS.gif|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | View: http://www.eurescom.de/~public-web-deliverables/P900-series/P921/D2/index.html for "live simulation" and "Cell Ranges for GSM1800 and UMTS Services" | ||
| + | |||
| + | (Source: Eurescom P921, D2) | ||
| + | |||
| + | == ⌘Network planning == | ||
| + | GSM versus UMTS | ||
| + | * UMTS is interference limited | ||
| + | * GSM is build on frequency reuse in the cells, while UMTS has the same frequency in neighbouring cells | ||
| + | * UMTS range is capacity limited | ||
| + | * UMTS requires simultaneous cell planning and network dimensioning | ||
| + | * handover is network based, the handset announces, network performs the handover | ||
| + | * In UMTS a mobile phone can be connected to two cells at the same time, the handover is then called soft handover. Handover between sectors in of the same antenna are called softer handover | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
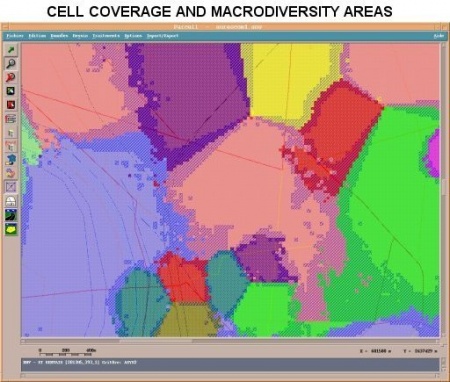
| + | == ⌘Cell cover and macro-diversity areas== | ||
| + | Outcome of Eurescom P921 system level simulations | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:CellCoverageUMTS.jpg|450px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | (Source: Eurescom P921, D2) | ||
| + | |||
| + | == ⌘Smart antennas and MIMO measurements== | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | [[File:SmartAntennaMeasures1.jpg]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | [[File:SmartAntennaMeasures2.jpg]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
= GSM = | = GSM = | ||
Revision as of 09:42, 21 September 2014
| Wiki for ITS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Contents
- 1 ⌘ Mobile Communication
- 1.1 ⌘Example of propagation
- 1.2 ⌘Oslo simulations, performed for GSM at 1800 MHz
- 1.3 ⌘Difference GSM - UMTS
- 1.4 ⌘Results of link level simulation
- 1.5 ⌘UMTS traffic simulations
- 1.6 ⌘Cell Breathing effect in UMTS
- 1.7 ⌘Network planning
- 1.8 ⌘Cell cover and macro-diversity areas
- 1.9 ⌘Smart antennas and MIMO measurements
- 2 GSM
- 3 UMTS specifications
⌘ Mobile Communication
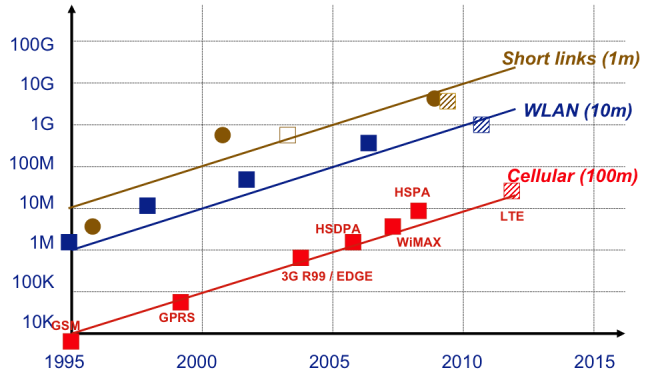
[Presentation G. Fettweis, IEEE VTC forum Baltimore], http://www.ieeevtc.org/plenaries/vtc2007fall/28.pdf
⌘Example of propagation
Results for UMTS (worst case), with 3 sector antenna
- Range of unloaded cell is 700 m in urban pedestrian
- With loaded cell, assumed increase of noise by 10 dB, max cell radius 390 m
- vehicular with typical range of 3600 m (unloaded) and 1900 m (loaded)
- Next: examples and simulations
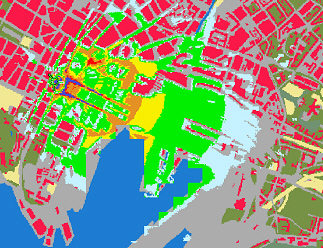
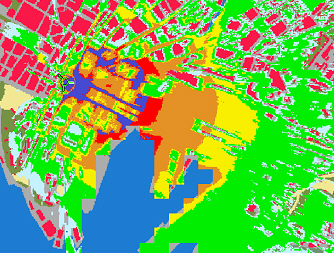
⌘Oslo simulations, performed for GSM at 1800 MHz
how much does the range decrease when reducing the power by 10 dB?
(Source: Helge Dommarsnes, Telenor Mobil)
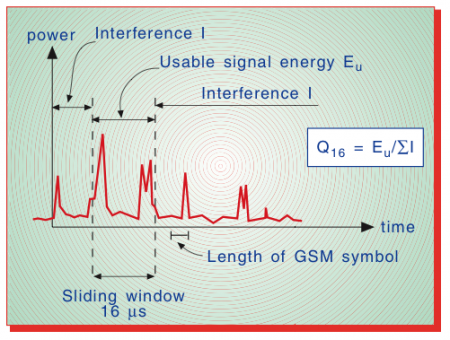
⌘Difference GSM - UMTS
- Frequency
- Receiver structure
- GSM sliding window of 16
- UMTS Rake receiver
- GSM sliding window of 16
Q16ratio:The ratio of the power inside to the power outside a window of duration 16 . For each IR the window is slid to find the position with highest power inside the window.
(Source:R Rækken, G. Løvnes, Telektronikk)
⌘Results of link level simulation
Simulations to achieve minimum W-CDMA using given QoS parameter: here voice service
(Source: Eurescom P921, D2)
⌘UMTS traffic simulations
(Source:Telenor FoU report 3-99)
⌘Cell Breathing effect in UMTS
View: http://www.eurescom.de/~public-web-deliverables/P900-series/P921/D2/index.html for "live simulation" and "Cell Ranges for GSM1800 and UMTS Services"
(Source: Eurescom P921, D2)
⌘Network planning
GSM versus UMTS
- UMTS is interference limited
- GSM is build on frequency reuse in the cells, while UMTS has the same frequency in neighbouring cells
- UMTS range is capacity limited
- UMTS requires simultaneous cell planning and network dimensioning
- handover is network based, the handset announces, network performs the handover
- In UMTS a mobile phone can be connected to two cells at the same time, the handover is then called soft handover. Handover between sectors in of the same antenna are called softer handover
⌘Cell cover and macro-diversity areas
Outcome of Eurescom P921 system level simulations
(Source: Eurescom P921, D2)
⌘Smart antennas and MIMO measurements
GSM
Example GSM: the upload band is from 880-915 Unik/MHz (in Europe), which is 35 Unik/MHz. With a carrier of 200 kHz we have 175 channels, which have to be divided between the various operators.