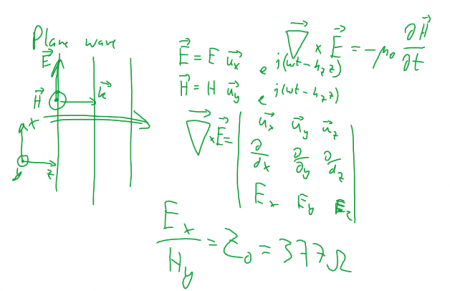Difference between revisions of "B1-Free Space Propagation"
Josef.Noll (Talk | contribs) |
Josef.Noll (Talk | contribs) m (Josef.Noll moved page B1 to B1-Free Space Propagation) |
(No difference)
| |
Revision as of 16:25, 21 September 2014
| Wiki for ITS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Contents
⌘ Maxwell's Equation in a source free environment
Source free environment and free space:
where div is a scalar function
and curl is a vector function
[Source: Wikipedia]
⌘ Wave equation
Taking the curl of Maxwell's equation
yields the wave equation:
with m/s
[Source: Wikipedia]
⌘ Homogeneous electromagnetic wave
single frequency
,
,
[Source: Wikipedia]
where
-
and
so?
-
is the imaginary unit
-
is the angular frequency, [rad/s]
-
is the frequency [1/s]
-
is Euler's formula
with and
⌘ Comments and tasks
- What is the difference between a static and a dynamic field
- Develop the relations for a plain wave
- Assume a plane wave:
. Show that
⌘ Task: Plane wave propagation
Assume a plane wave: . Show that
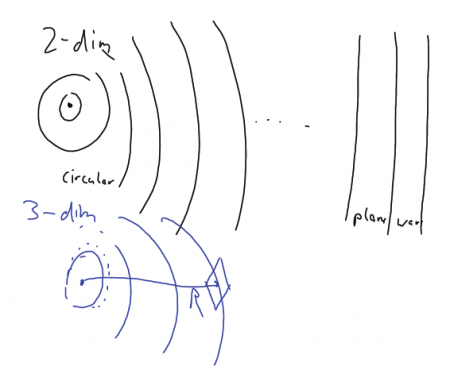
What is the relation between a plane wave and an omnidirectional wave?
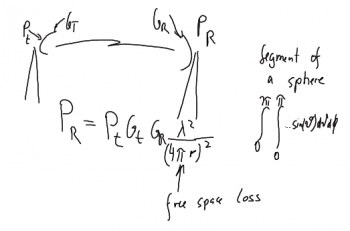
⌘ Free space propagation
develop propagation equation, see (http://www.antenna-theory.com/basics/friis.php)
Power received in an area in a distance R from transmitter:
- area of a sphere is
- power transmitted from isotropic antenna is
- antenna area of receiver is
- power received in A_r = P_r
thus
- convert into dB
- provide examples for f = 10 MHz, 1 GHz, 100 GHz
- discuss influences on radiation pattern
How much is 0 dB_m and 10 dB_m?
- Convert dBm to mW is: mW = 10^(x/10), x = number of dBm
- Convert mW to dBm is: dBm = 10*log10(y), y = number of mW
So you get:
- 0 dBm = 10^(0/10) = 1 mW
- 10 dBm = 10^(10/10) = 10 mW
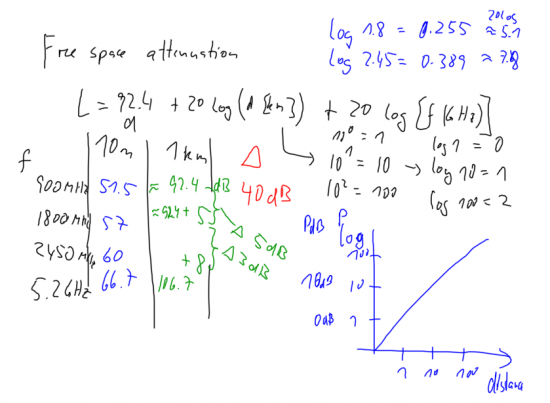
Free space attenuation
⌘Comments
|
Free space propagation from a transmit (t) to a receive (r) station. |
Calculation of free space attenuation. Note the increased free-space attenuation of approx 5 dB from 900 to 1800 Unik/MHz, and a further increase of 3 dB from 1800 (GSM 1800) to 2450 Unik/MHz (802.11b). Note also that increasing the distance by a factor of 10 will increase the power requirements by 20 dB.
Free space propagation Calculation: http://spreadsheets.google.com/pub?key=p0EyjWrbirGKJXK43uluJfg