TEK9530 - Measurable Security for the Internet of Things
| Wiki for ITS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
TEK9530 - Measurable Security for the Internet of Things
| TEK9530 | |
|---|---|
| News | given in spring |
| Organisation | ITS |
| by | György Kálmán |
| Keywords |
|---|
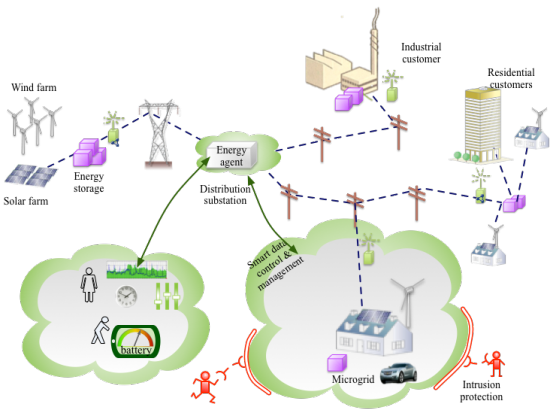
| Abstract | The course provides a methodology for measurable security, privacy, and dependability of industrial systems. Based on e.g. a smart grid example we will establish and develop the methodology to perform a multi-metrics analysis from components to sub-systems to systems. The course will allow you to compare security-related application goals with the results from the system analysis. |
|---|---|
| Objective (max 350 words) | After completing the course you will be able to:
|
| Keywords | Security, Network Security, Sensor Security, Sensor networks |
| Research Area(s) | Security |
| Type of course | PhD |
Upload TEK9530.png to see a course picture instead of the banner picture. Edit the page by Special:FormEdit/Course/TEK9530.
To add new lectures, use: Add a lecture
Info
Course page at UiO: https://www.uio.no/studier/emner/matnat/its/TEK9530/index.html
- This course is a PhD course. Please visit TEK5530 for the Master course.
- Evaluation is based on a presentation of topics and the implementation of your scenario.
- The Exam is performed orally, with info on TEK5530#Exam_2020
Topics
The course has the following lectures
- L1: Introduction
- L2: Internet of Things
- L3: Security of IoT
- L4: Smart Grid, Automatic Meter Readings (AMR)
- L5: Service implications on functional requirements
- L6: Technology mapping
- L7: Paper analysis with 15-20 min presentation
- L8: Practical implementation of ontologies
- L9: Logical binding - industrial example
- L10: Multi-Metrics Method for measurable Security
- L11: Multi-Metrics Weighting of an AMR sub-system
- L12: System Security and Privacy analysis
- L13: Phenomena "intrusion-detection"
- L14, L15: Real world examples
Introduction into Internet of Things (IoT)
This first part will provide the introduction into the Internet of Things (Lecture 1 - L2), with industrial examples
- Smart Grid and automatic meter system (AMS)
- Smart Homes with sensors
- Wireless System upgrade of cars
The part will further address potential security threats (L3), here given for the future smart grid.
When the future Smart Grid consists of Prosumers (Consumers, who might also be Producers) with different energy sources, the grid will become more unstable. We will use an example of an automatic meter reading (AMR) and -system (AMS) in L4 to address the security and privacy challenges.
The final part of this first block is addressed through lectures L5 and L6, and will create the mapping from functional requirements towards mapping into technology. Examples of such mapping are the translation of privacy requirements - can somebody see from my meter reading if I'm at home - towards technology parameters like how often are values read and published.
Machine-readable Descriptions
The next block is deals with the machine-readable description of security and privacy, security functionality and system of systems through ontologies.
- Establish system description examples of systems,
- Describing Security and Security Functionality in a semantic way
Application-driven security goals
This block will develop the security goals resulting from applications.
- From industrial examples, establish the functional requirements. Example: switch-off time of power circuits less than 10 ms
- From the functional requirements, select the security and privacy relations
- Establish application-driven security goals as well as the semantics of your system
Perform Multi-Metrics Analysis
This last block will analyse industrial examples based on the multi-metrics analysis
- Generate matrices to describe the security impact of components and sub-systems, and perform a multi-metrics analysis to establish the system security
- Analyze application goal versus system security and suggest improvements
Lecture overview with keywords
this section is automatically filled in based on the information on this MediaWiki