TEK5530 - Measurable Security for the Internet of Things
| Wiki for ITS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
TEK5530 - Measurable Security for the Internet of Things
| TEK5530 | |
|---|---|
| News | Lectures on Thursdays 0900-1200h, starting from 21Jan2016. The course is given at UNIK (Room 401), with video communication to Room Scheme@Ifi.UiO.no (1251) |
| Organisation | UNIK |
| by | Josef Noll, György Kálmán |
| Keywords |
|---|
| Abstract | The course provides a methodology for measurable security, privacy, and dependability of industrial systems. Based on e.g. a smart grid example we will establish and develop the methodology to perform a multi-metrics analysis from components to sub-systems to systems. The course will allow you to compare security-related application goals with the results from the system analysis. |
|---|---|
| Objective (max 350 words) | After completing the course you will be able to:
|
| Keywords | Security, Network Security, Sensor Security, Sensor networks |
| Research Area(s) | Security |
| Type of course | Master |
Upload TEK5530.png to see a course picture instead of the banner picture. Edit the page by Special:FormEdit/Course/TEK5530.
To add new lectures, use: Add a lecture
Info
- This course is a Master course. Please visit UNIK9750 for the PhD version of the course.
- The course takes place on Thursdays, 0900-1200h at UNIK. A video communication is available to Ifi, Room Scheme@Ifi.UiO.no (room 1251), see check: Video_conference
- We'll have video streaming: mms://lux.unik.no/401
- Evaluation is based on a presentation of topics and the implementation of your scenario.
Topics
The course has the following lectures
- 21Jan - L1: Introduction G,J
- Handouts Media:UNIK4750-L1-Introduction.pdf
- Lecture Notes Media:UNIK4750-L1-LectureNotes.pdf
- Podcast (Audio): Download lecture 1
- Video Podcast: Lecture 1 NB! If you are using Mac and have problem playing the video please first disable your firewall!
- 28Jan - L2: Internet of Things J
- Video introduction: IBM introduction to IoT, TED talk of John Barrett
- Handouts Media:UNIK4750-L2-Internet_of_Things.pdf, Internet of Things Paper (.pdf)
- Lecture Notes Media:UNIK4750-L2-LectureNotes.pdf
- Podcast (Audio - first 30 minutes): Download lecture 2
- Video Podcast: Lecture 2
- 4Feb - L3: Security in IoT G - Paper selection
- UNIK4750/List of papers, Guide on how to search for Literature
- Handouts Media:UNIK4750-L3-Security_IoT.pdf Devon conference paper (.pdf)
- no lecture notes
- Video Podcast: mms://lux.unik.no/UNIK4750-GK/UNIK-20160204.wmv
- 11Feb - L4: Smart Grid, Automatic Meter Readings (AMR) G
- Handouts Media:UNIK4750-L4-Automatic_Meter_Readings.pdf
- Video Podcast: mms://lux.unik.no/UNIK4750-GK/UNIK-20160211.wmv
- 18Feb - L5: Service implications on functional requirements G,(J)
- Handouts Media:UNIK4750-L5-Service_Implications.pdf
- Podcast (Audio): Download lecture 5
- Video Podcast: mms://lux.unik.no/UNIK4750-GK/UNIK-20160218.wmv Unfortunately due to technical problems the first half of the lecture is not recorded but you can use this link to download an audio file which covers the whole lecture.
- 25Feb - vinterferie
- 3Mar - L6: Technology mapping G,(J)
- Handouts Media:UNIK4750-L6-Technology_mapping.pdf,
- Video Podcast: mms://lux.unik.no/UNIK4750-GK/UNIK-20160303.wmv
- Paper: 10 differences between ICS and IT systems
- Paper: Practical applications of Lightweight Block Ciphers to Secure EtherNet/IP Networks
- Video Podcast: mms://lux.unik.no/UNIK4750-GK/UNIK-20160303.wmv
- 10Mar - L7: Paper analysis with 15-20 min presentation, evaluation criteria G,J
We will go over to the next presentation after exactly 20 min, due to the high number of presentations. Individual comments are given afterwards (in person or by phone)
- Please upload your slides by click on red link (login required). If you don't have a login, please ask Mehdi or Josef to create - or send us your .pdf file.
- Per Christian presents 2) K. Zhao and L. Ge, "A Survey on the Internet of Things Security"
- Media:Presentation_2_IoT_Survey_Per_Christian.pdf - slides by Per Christian
- Jostein Løvbråten presents 5) Roman, R., Najera, P., and Lopez, J., "Securing the Internet of Things"
- Media:Presentation_5_Securing_IoT_Jostein.pdf - slides by Jostein
- Marit Iren R. Tokle presents 8) - Khan, R., Khan, S.U., Zaheer, R., and Khan, S., "Future Internet: The Internet of Things Architecture, Possible Applications and Key Challenges"
- Kim Jonatan Wessel Bjørneset presents 12) Bruno, C., Guidi, L., Lorite-Espejo, A., and Pestonesi, D., "Assessing a Potential Cyberattack on the Italian Electric System"
- Angélique Colle presents 13) - Eckhoff, D. ; and Sommer, C., "Driving for Big Data? Privacy Concerns in Vehicular Networking"
- Media:Presentation_13_Privacy_BigData_Angelique.pdf - slides by Angelique
- Linn Eirin Paulsen presents 19) Wang, W., and Lu, Z., "Cyber security in the Smart Grid: Survey and challenges"
- Alina Lapina presents 24) Meltzer, D., "Securing the Industrial Internet of Things"
- Media:Presentation_24_Securing_Industrial_IoT_Alina.pdf - slides by Alina
- Raul Khaydarshin presents 25) Assessing the Security of Internet Connected Critical Infrastructures
- Media:Presentation_25_Security_CI_Raul.pdf - slides by Raul
- Farooq Abdullah presents 26) Securing the Internet of Things Infrastructure - standards and techniques
- Media:Presentation_26_Securing_IoT_Infrastructure_Farooq.pdf - slides by Farooq
- Mehdi Noroozi presents 27): Security of the Internet of Things: perspectives and challenges
- Presentation slides - slides by Mehdi
Sriramreddy Baddampresents 9) Trappe, W., Howard, R., and Moore, R.S., "Low-Energy Security: Limits and Opportunities in the Internet of Things"
Hafiz Muhammad Gulzarpresents 11) - Margulies, J., "Garage Door Openers: An Internet of Things Case Study"
- 17Mar - L8: Security Semantics J
- Handouts Media:UNIK4750-L8-Security_Semantics.pdf
- Lecture Notes Media:UNIK4750-L8-LectureNotes.pdf
- 24Mar - Easter Holidays
- 31Mar - L9: Logical binding - industrial example G,J, possible guest lecture
NB! Lecture will be held at room 308. IP for streaming is : 193.156.97.17
- Media:UNIK4750-L9-handouts.pdf - Handouts
- Media:20160331-L9-Lecture_notes.pdf Lecture notes
- Media:2016031-Project-Ideas.pdf - Information on your Project
- 7Apr - L10: Multi-Metrics Method for measurable Security J
- 14Apr - L11: Multi-Metrics Weighting of an AMR sub-system J
- 21Apr - L12: System Security and Privacy analysis J
- 28Apr - L13: Phenomena "intrusion-detection" - G
- 5May - Kristi Himmelfart - fridag
- 12May - L14: Real world examples - IoTSec infrastructure J
- 19May - L15: Real world IoT service evaluation group work J
- 26May - time for exam preparation (no lecture)
- 2Jun - Exam G,J
Introduction into Internet of Things (IoT)
This first part will provide the introduction into the Internet of Things (Lecture 1 - L2), with industrial examples
- Smart Grid and automatic meter system (AMS)
- Smart Homes with sensors
- Wireless System upgrade of cars
The part will further address potential security threats (L3), here given for the future smart grid.
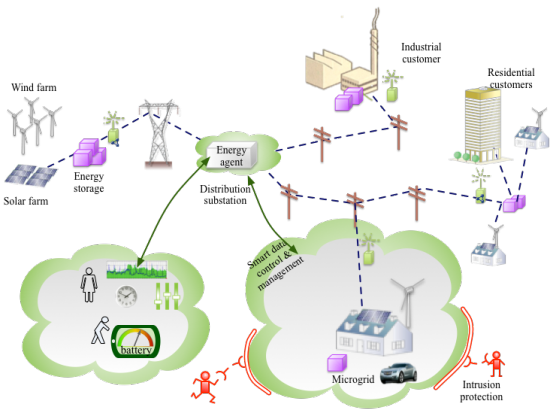
When the future Smart Grid consists of Prosumers (Consumers, who might also be Producers) with different energy sources, the grid will become more unstable. We will use an example of an automatic meter reading (AMR) and -system (AMS) in L4 to address the security and privacy challenges.
The final part of this first block is addressed through lectures L5 and L6, and will create the mapping from functional requirements towards mapping into technology. Examples of such mapping are the translation of privacy requirements - can somebody see from my meter reading if I'm at home - towards technology parameters like how often are values read and published.
Machine-readable Descriptions
The next block deals with the machine-readable description of security and privacy, security functionality and system of systems through ontologies.
- Establish system description examples of systems,
- Describing Security and Security Functionality in a semantic way
Application-driven security goals
This block will develop the security goals resulting from applications.
- From industrial examples, establish the functional requirements. Example: switch-off time of power circuits less than 10 ms
- From the functional requirements, select the security and privacy relations
- Establish application-driven security goals as well as the semantics of your system
Perform Multi-Metrics Analysis
This last block will analyse industrial examples based on the multi-metrics analysis.
- Generate matrices to describe the security impact of components and sub-systems, and perform a multi-metrics analysis to establish the system security
- Analyze application goal versus system security and suggest improvements
Lecture overview with keywords
this section is automatically filled in based on the information on this MediaWiki