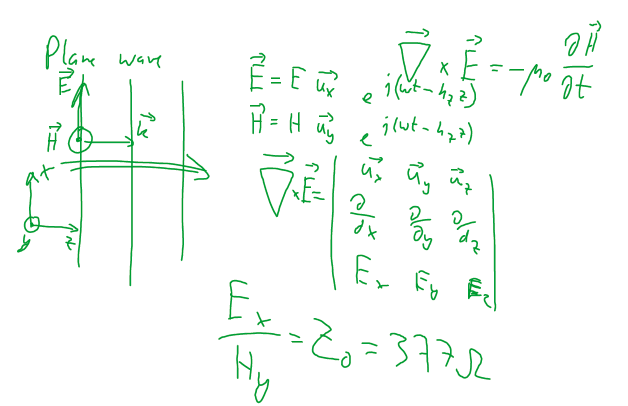UNIK4700/UNIK9700 Signal and Capacity
Josef Noll,
UNIK 4700: Radio & Mobility
3rd lecture block
- Free space propagation equation, what is the power level at a receive antenna, see Media:PropagationConstant.pdf for a more detailed explanation of the terms being used here
- Capacity of mobile and wireless propagation,
Signal Strength and Capacity
A4-Signal Strength and Capacity
Main focus in the previous lectures was on propagation effects. We will first repeat the main conclusions from last lecture on electromagnetic signals, and then introduce the capacity of a system based on Shannon's theorem.
New literature:
- J. Noll, K. Baltzersen, A. Meiling, F. Paint , K. Passoja, B. H. Pedersen, M. Pettersen, S. Svaet, F. Aanvik, G. O. Lauritzen. '3rd generation access network considerations'. selected pages from FoU R 3/99, Jan 1999
- H. Holma, A. Toskala (eds.), "WCDMA for UMTS", John Wiley & sons, Oct 2000, selected pages
Signal/noise ratio
,
where P is average power
- why talking about noise?
- dB,
- near-far problem
[source: Wikipedia]
Shannon Theorem
- The fundamental theorem of information theory, or just Shannon's theorem, was first presented by Claude Shannon in 1948.
- Given a noisy channel with channel capacity C and information transmitted at a rate R, then if R < C there exist codes that allow the probability of error at the receiver to be made arbitrarily small. This means that theoretically, it is possible to transmit information nearly without error at any rate below a limiting rate, C.
- See File:LarsLundheim-Telektronikk2002.pdf: The channel capacity of a band-limited information transmission channel with additive white, Gaussian noise. This capacity is given by an expression often known as “Shannon’s formula”:
[bits/s]
with W as system bandwidth, and in case of interference free environment, otherwise
, where
with
as Boltzmann constant and
as temperature in Kelvin.
Shannon - formula
[bits/s]
Exercises
- calculate capacity for W= 200 kHz, 3.8 MHz, 26 MHz, (all cases P/N = 0 dB, 10 dB, 20 dB)
- If the SNR is 20 dB, and the bandwidth available is 4 kHz, what is the capacity of the channel?
- If it is required to transmit at 50 kbit/s, and a bandwidth of 1 MHz is used, what is the minimum S/N required for the transmission?
[source: Wikipedia, Telektronikk 2002]
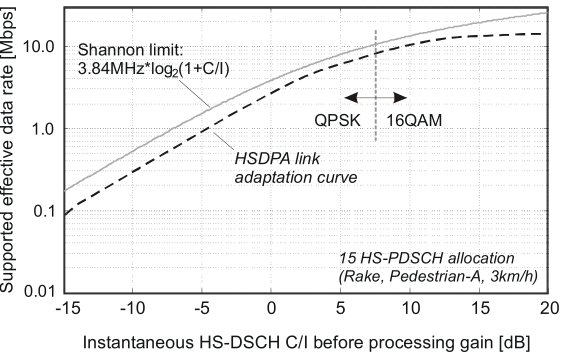
Cell capacity in UMTS
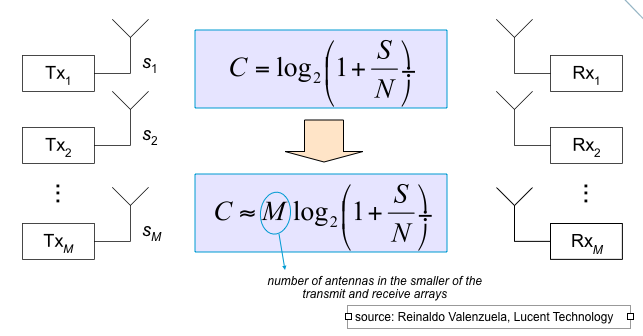
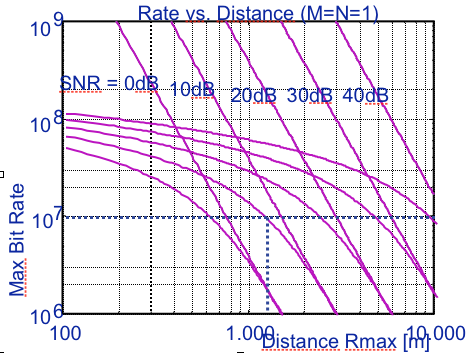
Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output: MIMO
Free Space Propagation
Maxwell's Equation in a source free environment
Source free environment and free space:
where div is a scalar function
and curl is a vector function
[Source: Wikipedia]
Wave equation
Taking the curl of Maxwell's equation
yields the wave equation:
with m/s
[Source: Wikipedia]
Homogeneous electromagnetic wave
A single frequency electro (E)-magnetic (B) wave is described by
,
,
[Source: Wikipedia]
where
-
and
so?
-
is the imaginary unit
-
is the angular frequency, [rad/s]
-
is the frequency [1/s]
-
is Euler's formula
with the group velocity (free space = speed of light) and
the refraction index
Tasks
Free space propagation
Power received in an area in a distance R from transmitter:
- area of a sphere is
- power transmitted from isotropic antenna is
- antenna area of receiver is
- power received in A_r = P_r
thus
- convert into dB
- provide examples for f = 10 MHz, 1 GHz, 100 GHz
- discuss influences on radiation pattern
Tasks
Develop the propagation equation, see (http://www.antenna-theory.com/basics/friis.php)
How much is 0 dB_m and 10 dB_m?
- Convert dBm to mW is: mW = 10^(x/10), x = number of dBm
- Convert mW to dBm is: dBm = 10*log10(y), y = number of mW
So you get:
- 0 dBm = 10^(0/10) = 1 mW
- 10 dBm = 10^(10/10) = 10 mW
Free space attenuation