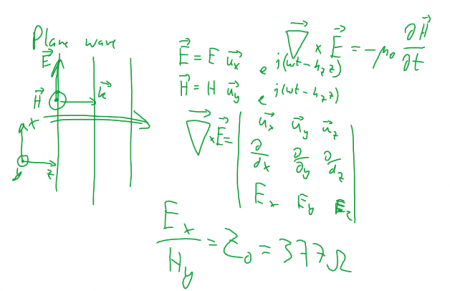B1-Free Space Propagation
| Wiki for ITS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Contents
⌘ Maxwell's Equation in a source free environment
Source free environment and free space:
where div is a scalar function
and curl is a vector function
[Source: Wikipedia]
⌘ Wave equation
Taking the curl of Maxwell's equation
yields the wave equation:
with m/s
[Source: Wikipedia]
⌘ Homogeneous electromagnetic wave
single frequency
,
,
[Source: Wikipedia]
where
-
and
so?
-
is the imaginary unit
-
is the angular frequency, [rad/s]
-
is the frequency [1/s]
-
is Euler's formula
with and
⌘ Comments and tasks
- What is the difference between a static and a dynamic field
- Develop the relations for a plain wave
- Assume a plane wave:
. Show that
Question: I still don't understand the propagation equation
⌘ Task: Plane wave propagation
Assume a plane wave: . Show that
What is the relation between a plane wave and an omnidirectional wave?
⌘ Free space propagation
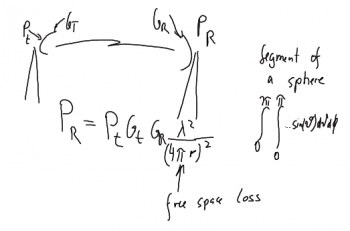
develop propagation equation, see (http://www.antenna-theory.com/basics/friis.php)
Power received in an area in a distance R from transmitter:
- area of a sphere is
- power transmitted from isotropic antenna is
- antenna area of receiver is
- power received in A_r = P_r
thus
- convert into dB
- provide examples for f = 10 MHz, 1 GHz, 100 GHz
- discuss influences on radiation pattern
How much is 0 dB_m and 10 dB_m?
- Convert dBm to mW is: mW = 10^(x/10), x = number of dBm
- Convert mW to dBm is: dBm = 10*log10(y), y = number of mW
So you get:
- 0 dBm = 10^(0/10) = 1 mW
- 10 dBm = 10^(10/10) = 10 mW
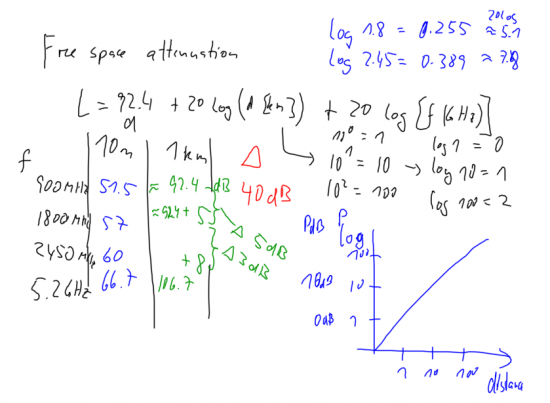
Free space attenuation
⌘Comments
|
Free space propagation from a transmit (t) to a receive (r) station. |
Calculation of free space attenuation. Note the increased free-space attenuation of approx 5 dB from 900 to 1800 Unik/MHz, and a further increase of 3 dB from 1800 (GSM 1800) to 2450 Unik/MHz (802.11b). Note also that increasing the distance by a factor of 10 will increase the power requirements by 20 dB.
Have in mind that normal communication is always worse than the "ideal" free space communication. You have shadowing, reflections, interference, and other influences increasing the path loss. An example is the Bluetooth communication between your mobile phone and your headset, where your body absorbs energy and shadows for direct communication.
Free space propagation Calculation: http://spreadsheets.google.com/pub?key=p0EyjWrbirGKJXK43uluJfg