D2-Short Range Systems
From its-wiki.no
Revision as of 20:40, 21 September 2014 by Josef.Noll (Talk | contribs)
| Wiki for ITS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Contents
⌘ Short range communication
Short range communication systems covers both industrial and end-customer applications, and is often used for sensor communications.
Presentations from earlier years
Wireless HART, ++ISO100
- Media:HART_ISO100.pdf (by Johan Tresvig)
- Book: WirelessHART - Applying wireless technology in real-time industrial process control
- Media:A Comparison of WirelessHART and ZigBee for Industrial Applications.pdf
- Media:A Location-determination Application in WirelessHART.pdf
- Media:Comparison of Industrial WSN Standards.pdf
- Media:WirelessHART - Applying wireless technology in real-time industrial process control.pdf
see also earlier lecture WiMAX_and_WirelessHART
- Wireless HART Overview: Media:HART_overview.pdf
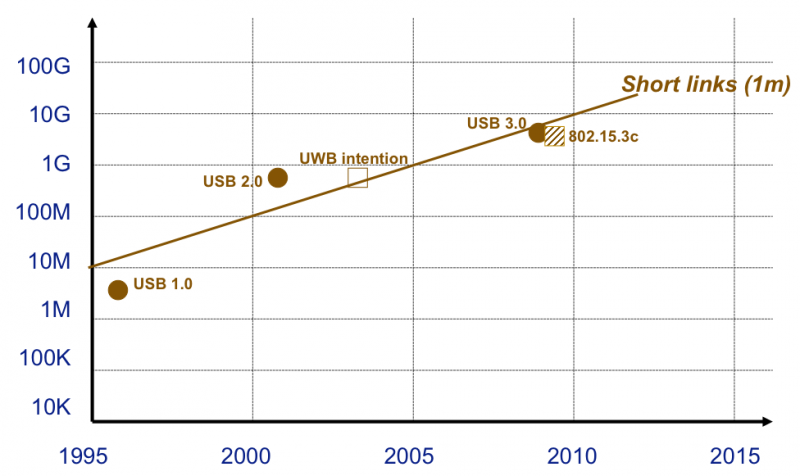
⌘ USB speed
[Presentation G. Fettweis, IEEE VTC forum Baltimore], http://www.ieeevtc.org/plenaries/vtc2007fall/28.pdf
Test yourself, answer these questions
- What is WirelessHART?
- What radio technology is used (WirelessHART)?
- What network topologies are supported (WirelessHART)?
- What are the main parts of a WiHART network?
- How does channel hopping work?