Difference between revisions of "E1-Mobile Network mobility"
From its-wiki.no
Josef.Noll (Talk | contribs) (→Mobility principles) |
Josef.Noll (Talk | contribs) (→GSM Handover) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
* Mobility | * Mobility | ||
| + | = GSM Handover types = | ||
| + | Network-controlled, mobile terminal assisted handover | ||
| + | * The network takes the handover decisions | ||
| + | * The mobile terminal supervises and reports its signal quality | ||
| + | |||
| + | Four types of handover | ||
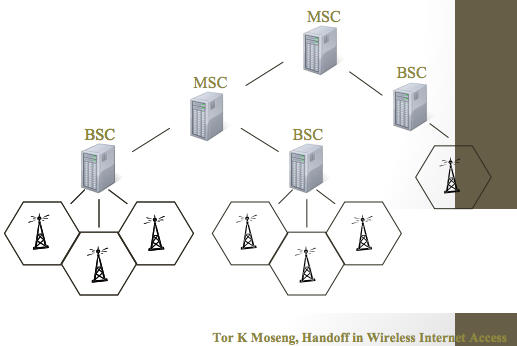
| + | * Intra BTS handover | ||
| + | * Intra-BSC handover | ||
| + | * Inter-BSC handover | ||
| + | * Inter-MSC handover | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Handover_scenario_GSM.png|handover scenario GSM]] | ||
= GSM Handover = | = GSM Handover = | ||
| − | + | Mechanisms for requesting hand-over | |
| − | + | * power lever in handset is too low | |
| − | + | * signal/noise ratio is too low | |
| − | + | * bit-error-rate is too high | |
| − | + | * ... | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Procedure | |
| − | + | * handset requires hand-over | |
| − | + | * base-station decides | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Alternatives | |
| − | + | * hand-over to neighbour cell | |
| + | * hand-over to different RNC/BSC | ||
| + | * first registration (roaming) | ||
= References = | = References = | ||
Revision as of 21:14, 20 November 2014
| Wiki for ITS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Contents
E1 - Mobile Network mobility
Mobility principles
- Continuous mobility enables continuous availability of services while the user moves
- Discrete mobility enables the availability of services within certain areas and for certain access points, e.g home and office, but not while moving from one area to another.
- Portability is an example of discrete terminal mobility, where it is only allowed to move a terminal from one plug to another.
Handover
Handover: Changing the point of connection while communicating
- When a mobile user travels from one area of coverage or cell to another cell within a call’s duration the call should be transferred to the new cell’s base station
Why handover is needed?
- Mobility
GSM Handover types
Network-controlled, mobile terminal assisted handover
- The network takes the handover decisions
- The mobile terminal supervises and reports its signal quality
Four types of handover
- Intra BTS handover
- Intra-BSC handover
- Inter-BSC handover
- Inter-MSC handover
GSM Handover
Mechanisms for requesting hand-over
- power lever in handset is too low
- signal/noise ratio is too low
- bit-error-rate is too high
- ...
Procedure
- handset requires hand-over
- base-station decides
Alternatives
- hand-over to neighbour cell
- hand-over to different RNC/BSC
- first registration (roaming)
References
- Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems http://www.ieee802.org/21/archived_docs/Documents/OtherDocuments/Handoff_Freedman.pdf
- LTE Handover: http://reference.kfupm.edu.sa/content/d/e/design_and_evaluation_of_a_handover_deci_72726.pdf
- Handover between GSM & UMTS : http://www.ericsson.com/ne/res/thecompany/docs/publications/ericsson_review/2003/2003011.pdf
- Soft Handovers in CDMA tech.: [1]
Presentations
Basics of Handover, examples from GSM and UMTS
- Media:Basics_Handover.pdf (by Naji Ahmed Kadah)
- Media:Basics_Handover_comments.pdf