Difference between revisions of "E2-IP Mobility"
Josef.Noll (Talk | contribs) |
Josef.Noll (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
= Macro versus Micro Mobility = | = Macro versus Micro Mobility = | ||
| − | [[File:Macro_Micro_Mobility.png | + | [[File:Macro_Micro_Mobility.png|Source:Alam2000]] |
= Mobile IP Mobility = | = Mobile IP Mobility = | ||
| − | [[File:Mobile_IP_overview.png | + | [[File:Mobile_IP_overview.png|Mobile IP Mobility]] |
Mobile IP – the long term vision (also for mobile networks) | Mobile IP – the long term vision (also for mobile networks) | ||
* HA, FA | * HA, FA | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
= Mobile IPv4 Triangular routing = | = Mobile IPv4 Triangular routing = | ||
| − | [[File:Mobile_IP_triangular routing.png | + | [[File:Mobile_IP_triangular routing.png|Mobile IP Mobility]] |
* Correspondent does not know IP address of "moved" device, thus sends a request to the HA | * Correspondent does not know IP address of "moved" device, thus sends a request to the HA | ||
* HA forwards to the moved device via Foreign Agent (FA) | * HA forwards to the moved device via Foreign Agent (FA) | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
= Heterogeneous network mobility = | = Heterogeneous network mobility = | ||
| − | [[File:Heterogeneous_network_mobility.png | + | [[File:Heterogeneous_network_mobility.png|Heterogeneous Network mobility]] |
* combines IP and mobile components | * combines IP and mobile components | ||
* challenge: credential distribution | * challenge: credential distribution | ||
Revision as of 21:05, 20 November 2014
| Wiki for ITS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Contents
E2-IP Mobility
Main components
- Home Agent (HA)
- Foreign Agent (FA)
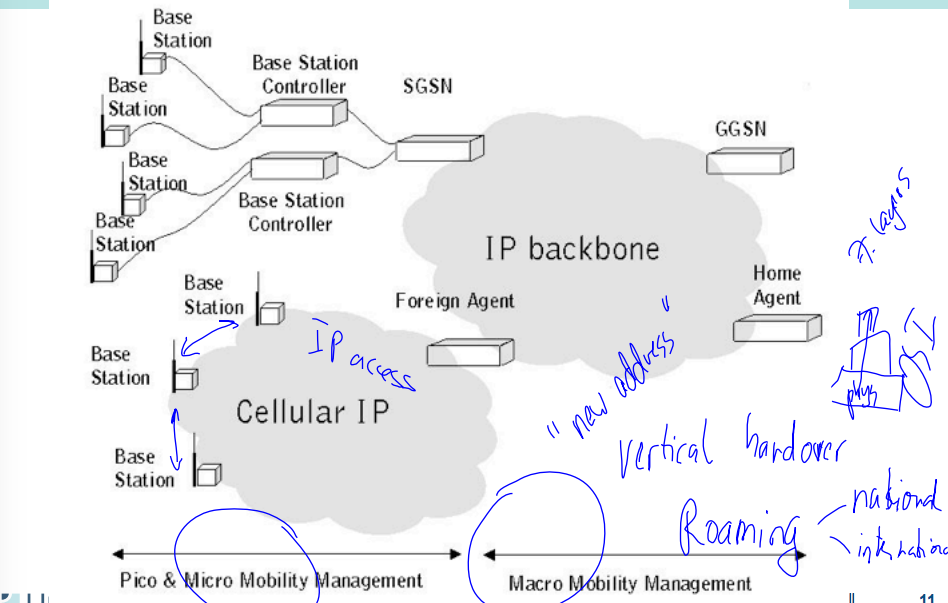
Macro versus Micro Mobility
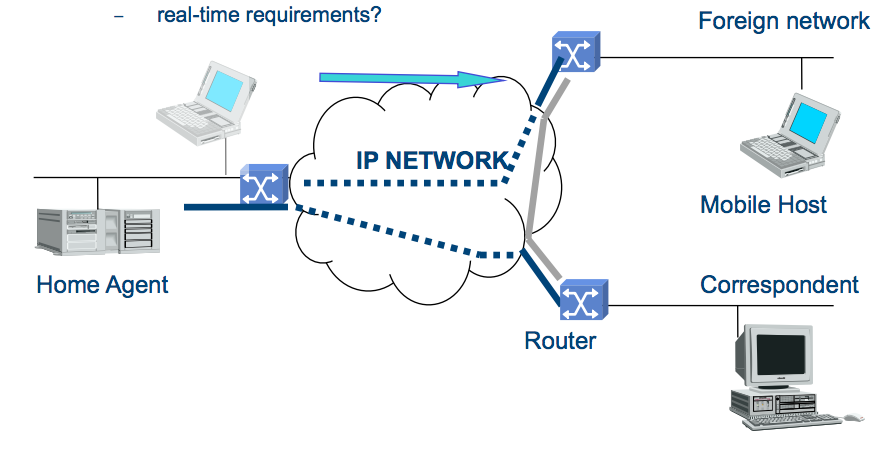
Mobile IP Mobility
 Mobile IP – the long term vision (also for mobile networks)
Mobile IP – the long term vision (also for mobile networks)
- HA, FA
- IPv6
- real-time requirements?
Mobile-IP developments
- IDMP - intra-domain mobility protocoll
- Hawaii
- Cellular IP, Cellular IPv6 (CIPv6)
- Hierarchical Mobile IPv6 (HMIPv6)
- Fast Mobile IPv6
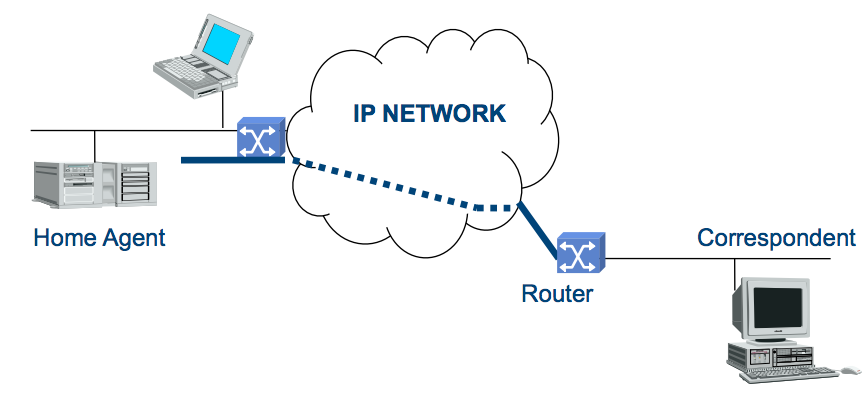
Mobile IPv4 Triangular routing
- Correspondent does not know IP address of "moved" device, thus sends a request to the HA
- HA forwards to the moved device via Foreign Agent (FA)
- Moved device answers directly to the Correspondent
Mobile IPv4 to Mobile IPv6
- replace triangular routing, keep address
- route optimisation
- defined for low-speed mobility
Intra-domain mobility
- Host based routing
- Data integrity protection,
Security
- Sender authentication,
- Data integrity protection,
- Replay protection
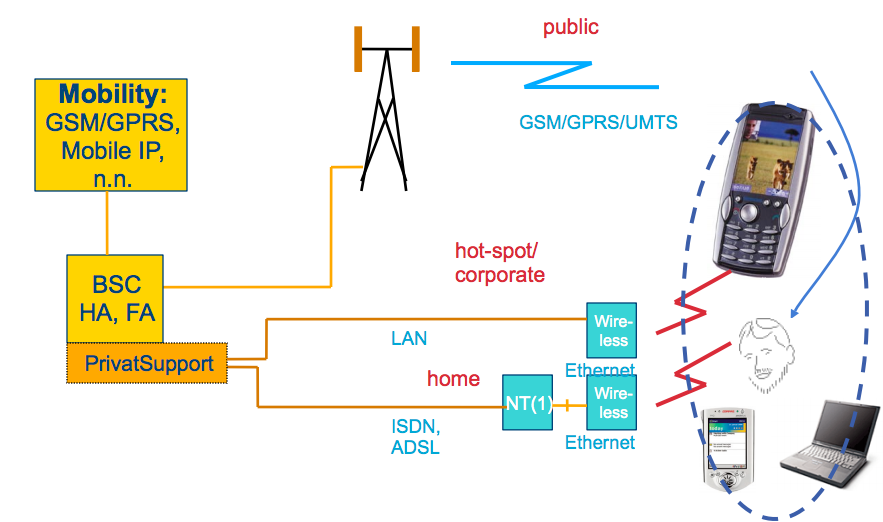
Heterogeneous network mobility
- combines IP and mobile components
- challenge: credential distribution
References
- [Ala2000] Sami Ala-Luukko, "Mobility
Management in IETF and GPRS Specifications", May 2000, Helsinki University of Technology, http://www.tml.tkk.fi/Opinnot/ Tik-110.551/2000/papers/ management_in_IETF/iwork.htm % introductory reading micro-/macro-mobility
- [Paint2000] Frederic Paint, Geir Egeland,
"Seamless Mobility in IP Networks", Telektronikk 1.2001, pp 083-091 % introductory reading
- [Akyildiz2004] Ian F. Akylidiz, Jiang Xie, and
Shantidev Mohanty, "A survey of Mobility management in Next-Generation all-IP based wireless systems", IEEE Wireless Communications, Aug 2004, pp 16-28
- [Ferreira2008] Ferreira, N.G.; Sargento, S.;
Aguiar, R.; Implementation and experimental evaluation of a fast local mobility protocol, Computers and Communications, 2008. ISCC 2008. IEEE Symposium on 6-9 July 2008 Page(s):757 - 763
- [Lee2008] Global Mobility Management
Scheme with Interworking between PMIPv6 and MIPv6, Networking and Communications, 2008. WIMOB '08. IEEE International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, 12-14 Oct. 2008 Page(s):153 - 158
- [Aho2008] Aho, K.; Aijanen, J.; Ristaniemi, T.;
Impact of Mobility to the VoIP over HSUPA System Level Performance, Vehicular Technology Conference, 2008. VTC Spring 2008. IEEE 11-14 May 2008 Page(s):2091 - 2095